vlc and its use cases and application brief description
Clock & p2p
Verifiable logic clock & vlc and its use cases.
vlc and its use cases and application brief description
Prerequisites
Lamport clock
The Lamport clock is a logical clock used to order events in a distributed system. It provides a way to capture the "happens-before" relationship between events, which is essential for understanding causality.
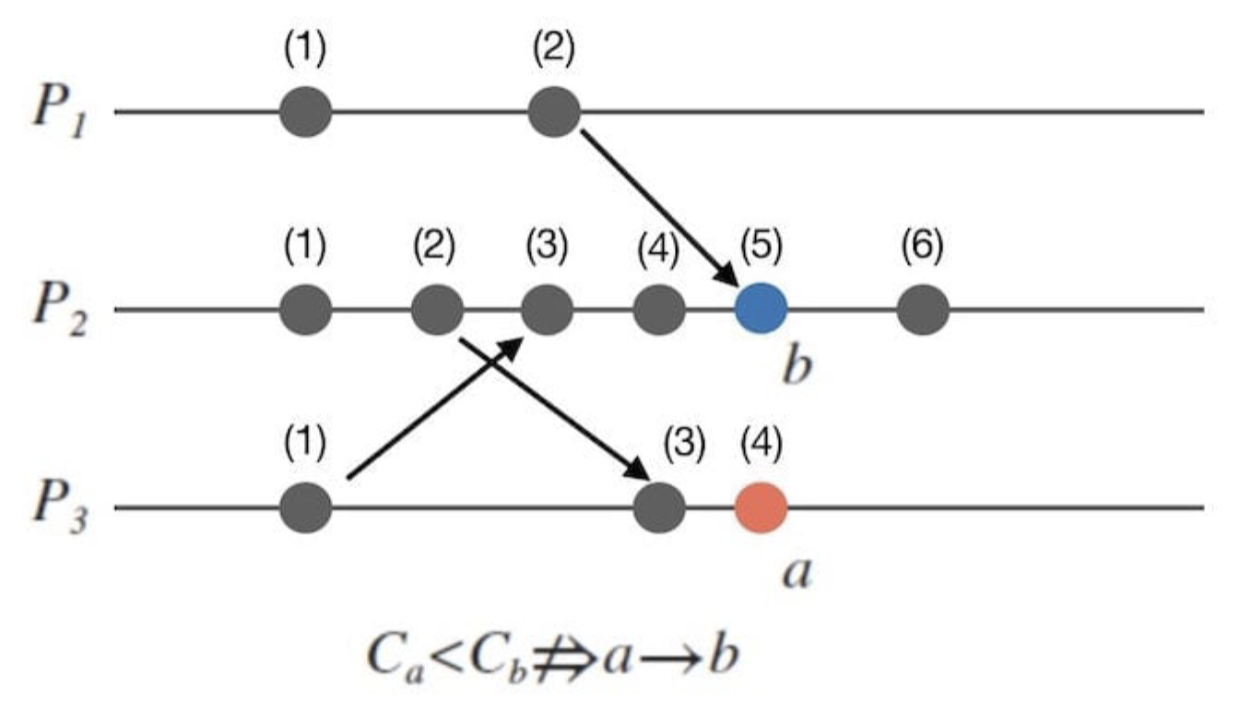
Examples
Consider two processes, P1 and P2:
- P1 starts with a clock value of 1, performs an event (clock becomes 2), and sends a message to P2 with the timestamp 2.
- P2 receives the message with timestamp 2, and updates its clock to
max(current clock, 2) + 1(e.g., if P2's current clock was 1, it becomes 3).
Conclusions
Cannot capture concurrent events(events that are not causally related).- As shown in the above picture,
events a and b
- As shown in the above picture,
- It constructs
fail to workin an open network withByzantine participants.
Vector clock
Vector clocks are an extension of Lamport clocks that provide more detailed information about the causality of events. Each process maintains a vector of clock values, one for each process in the system.
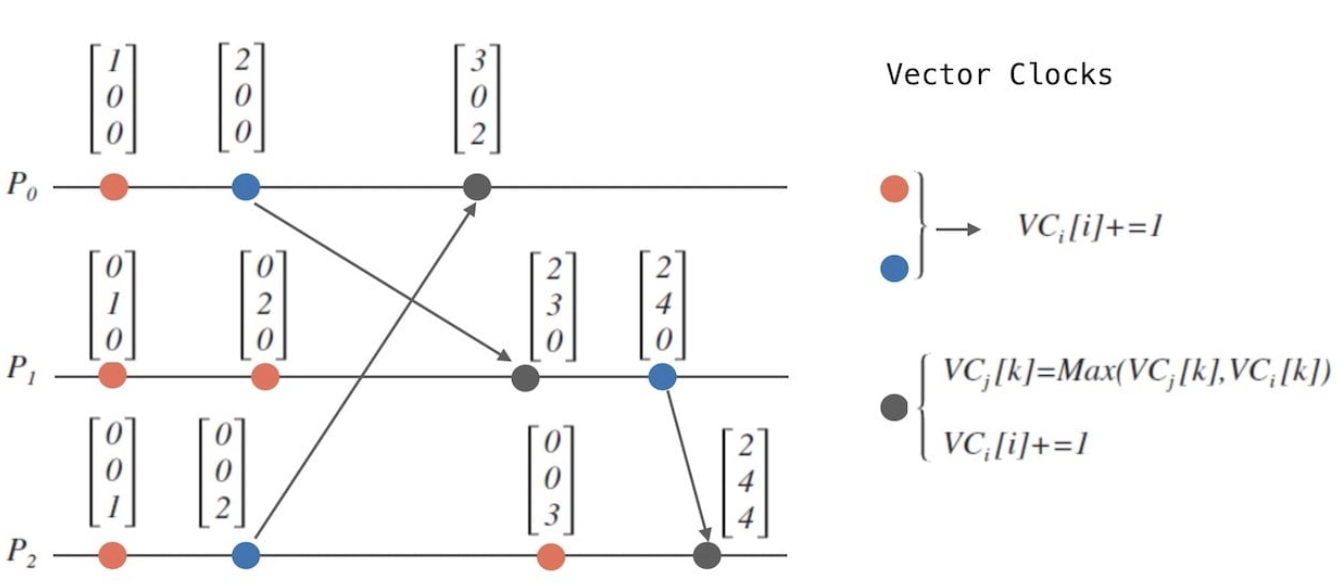
Examples
Consider two processes, P1 and P2:
- P1's vector clock is initially
[0, 0]. It performs an event, updating to[1, 0], and sends a message to P2. - P2's vector clock is
[0, 0]. Upon receiving the message with vector clock[1, 0], it updates to[1, 1](assuming it performs an event after receiving).
Conclusions
- It constructs
fail to workin an open network withByzantine participants.
VLC (Verifiable Logical Clock)
Without reliable logical clocks, systems and applications are forced to use expensive BFT SMR protocols which enforces total order of requests, even though their application semantics may only require partial ordering guarantees.
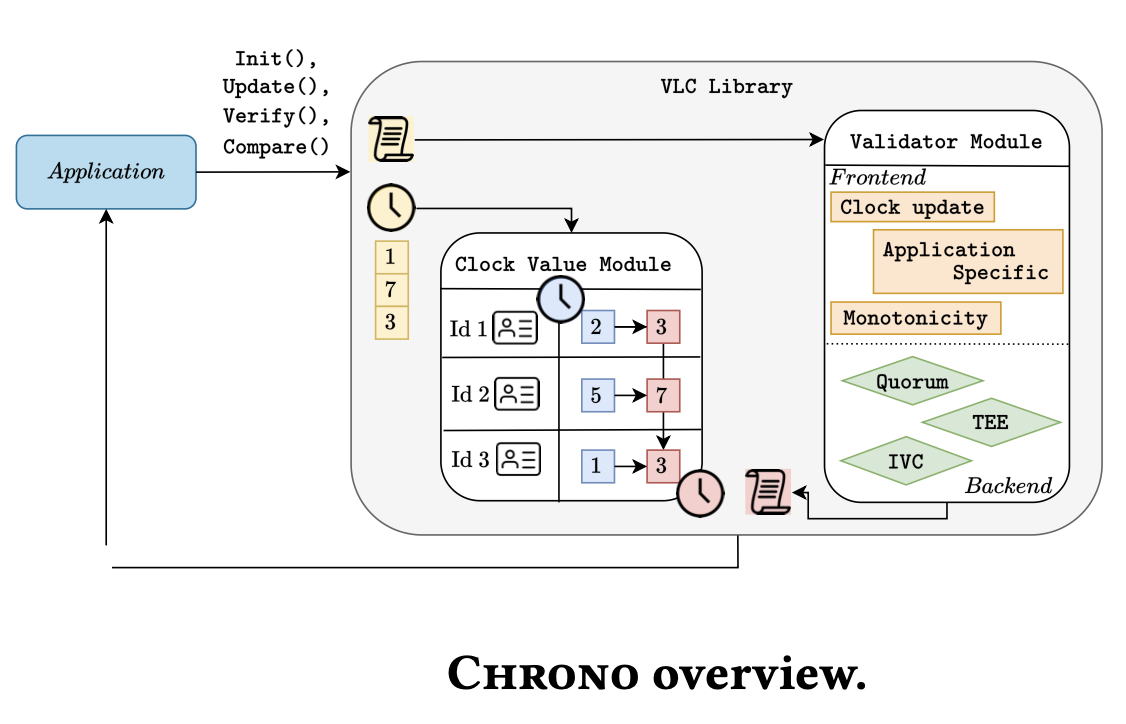
Chrono overview
So, vlc (verifiable logical clock) is construct atop on vector clock, and add the verifiable proof feature. The chrono is as a concrete instance of VLC. More detail could read the paper of Building a Verifiable Logical Clock for P2P Networks
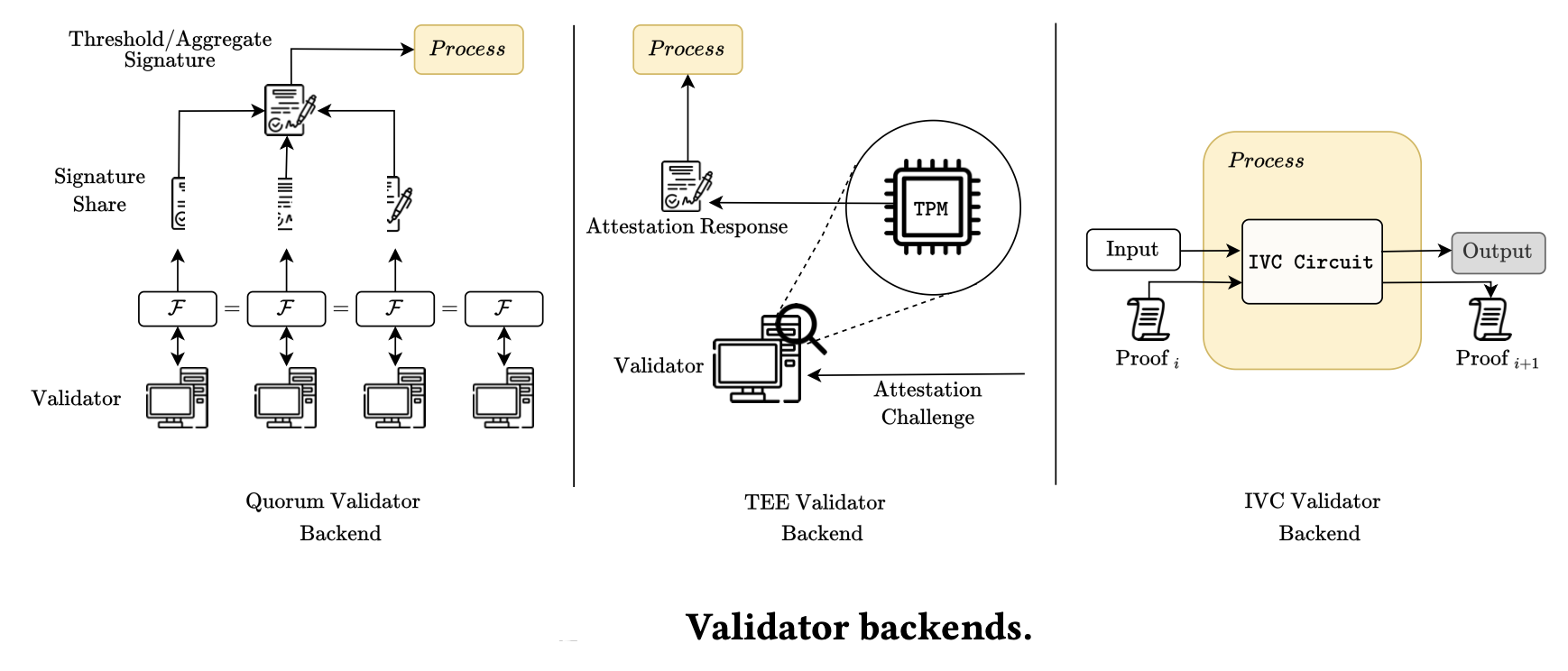
Validator backends
Applications & use cases
Two use cases, causally Consistent Data Store and mutual exclusion, are introduced in detail in paper.
Regular logical clock use case
Regular logical clock have been applied in many scenarios. As follows:
- Weakly consistent storage systems
- (
Cops: causally Consistent Data Store)
- (
- Causally ordered broadcast
- Deadlock detection
- (
Mutual exclusionof shared resources in a distributed system) - Bakery algorithm
- (
- Distributed snapshots
- Distributed system debugging.
VLC implement’s use cases
Cops: causally Consistent Data StoreMutual exclusion
- vlc and its use cases and application brief description
- Prerequisites
- Lamport clock
- Examples
- Conclusions
- Vector clock
- Examples
- Conclusions
- VLC (Verifiable Logical Clock)
- Chrono overview
- Validator backends
- Applications & use cases
- Regular logical clock use case
- VLC implement’s use cases